What Is Groundworks? Groundworks Construction Explained
Groundworks are the preparatory construction works carried out below ground level before a building’s structure begins.
In simple terms, groundworks create a stable base that supports the entire building. This includes excavation, drainage installation, service connections, and foundation construction.
Every successful residential, commercial, or basement development depends on properly engineered groundworks construction.
What Is Included in Groundworks?
Groundworks typically include:
Site clearance and enabling works
Excavation and earthworks
Soil assessment and preparation
Drainage and attenuation systems
Underground utility installation
Foundations and reinforced concrete substructures
Without correctly executed groundworks, buildings are at risk of structural movement, settlement, and water ingress.
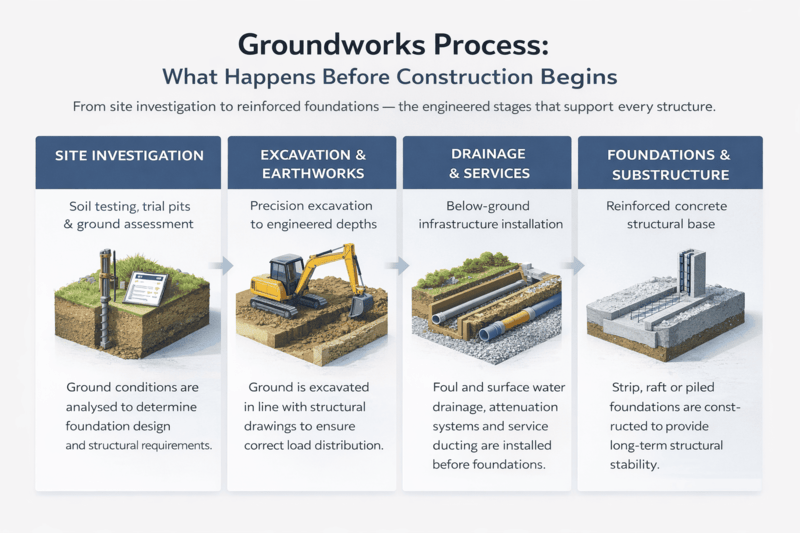
The Groundworks Construction Process: Step by Step
-
Before excavation begins, soil conditions are assessed. This may involve trial pits, boreholes, and classification of ground type.
In areas such as London, clay-heavy soils require careful consideration due to expansion and shrinkage risks.
Foundation design must respond to ground conditions - not assumptions.
-
Vegetation, debris, and existing structures are removed. Access routes and temporary works are established to ensure safe and compliant operations.
This stage prepares the site for controlled excavation.
-
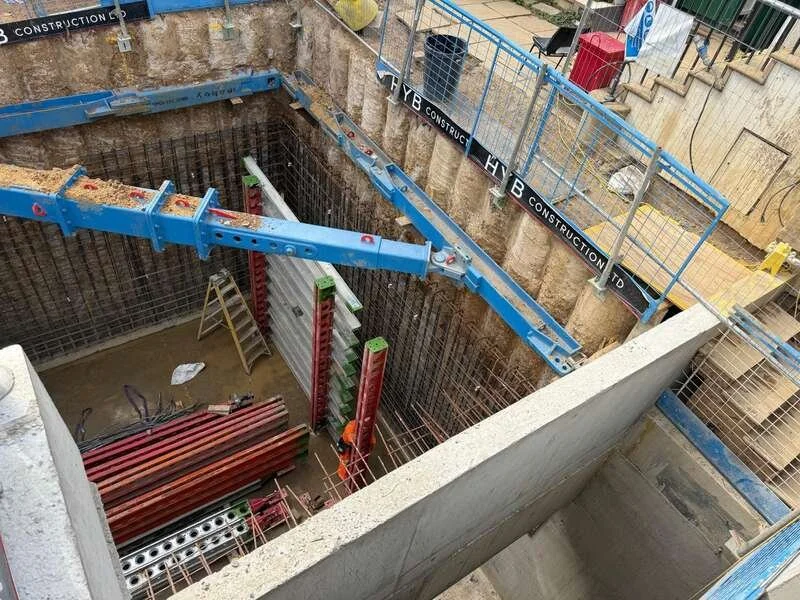
Excavation is carried out to engineered depths specified in structural drawings.
Accuracy at this stage ensures:
Correct load distribution
Compliance with foundation design
Stability for adjacent structures
On constrained urban sites, temporary support systems such as shoring or underpinning may be required.
-
Before foundations are poured, drainage systems are installed.
This includes:
Foul and surface water drainage
Soakaways and attenuation tanks
Underground ducting for utilities
Incorrect gradients or inadequate compaction can lead to long-term flooding and structural issues.
-
Foundation types vary depending on load requirements and soil conditions. Common examples include:
Strip foundations
Raft slabs
Piled foundations
Reinforced concrete bases
This phase integrates closely with steel fixing and formwork to ensure structural strength.
Why Quality Groundworks Matter
Groundworks failures often become visible years after construction.
Common consequences of inadequate groundworks include:
Differential settlement
Cracked walls and masonry
Foundation instability
Water penetration
Drainage system failure
Remedial works at substructure level are significantly more expensive than prevention.
For this reason, experienced groundworks contractors prioritise inspection, testing, and strict procedural control.
Groundworks in London: Additional Considerations
Urban projects introduce added complexity:
Restricted site access
Party wall constraints
High water tables
Historic made ground
Proximity to neighbouring foundations
Selecting experienced groundworks contractors in London reduces these risks through structured sequencing and engineering oversight.
How Professional Groundworks Are Quality Controlled
At HYB Construction Ltd, groundworks are treated as a critical engineering phase.
Typical quality procedures include:
Soil classification and review
Engineer inspection of foundation trenches
Compaction testing
Drainage pressure testing
Waterproofing coordination for basements
This ensures regulatory compliance and long-term structural stability.
FAQs About Groundworks
-
Groundworks are the below-ground construction activities completed before a building’s superstructure begins. This includes excavation, drainage installation, utility services, and foundation construction.
-
Small residential projects may take 1–3 weeks. Larger developments or basement excavations can take several months depending on soil conditions and structural complexity.
-
Groundworks costs vary depending on excavation depth, soil type, access constraints, and foundation design. Urban London sites often involve additional structural and logistical requirements.
-
Groundworks provide the structural base for a building. Poorly executed groundworks can cause settlement, cracking, flooding, and long-term instability.
-
Yes. Structural engineers typically inspect trenches before concrete is poured. Compaction and drainage testing are also standard practice on professionally managed sites.
Conclusion
Understanding what groundworks are - and ensuring they are carried out correctly - is essential for any successful construction project. From site investigation and excavation to drainage installation and reinforced foundations, properly executed groundworks provide the structural base that supports everything built above.
Whether for residential developments, basement projects or large commercial schemes, professional groundworks construction plays a critical role in delivering long-term structural stability and regulatory compliance. Getting the substructure right from the outset reduces the risk of settlement, water ingress and costly remedial work later in the build process.
If you’re planning a development and want to understand how engineered groundworks support reinforced concrete construction, explore our Groundworks Services to see how we deliver stable, compliant substructures across London projects.